In today’s competitive landscape, efficiency isn’t just an advantage, it’s a core requirement for growth. Businesses are constantly seeking ways to eliminate repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and free up talented teams for strategic, high-value work. This is where business process automation (BPA) transitions from a complex, enterprise-level concept to a practical, accessible strategy for companies of all sizes. But what does it actually look like in practice?
Forget abstract theories. This article gets straight to the point, diving deep into tangible business process automation examples across critical functions like finance, HR, and marketing. We won’t just list them; we’ll dissect how these automated workflows operate, analyze the strategic advantages they unlock, and provide actionable takeaways you can implement.
You’ll see how specific automations, from streamlining invoice processing to optimizing customer onboarding, can fundamentally change how your business operates. We will break down replicable strategies and highlight how a strategic partner can help implement tailored solutions, such as powerful custom ERPs, to streamline these very processes and drive meaningful results. This guide is your blueprint for turning automation from a buzzword into a powerful operational reality.
1. Customer Onboarding Automation
Customer onboarding automation transforms the initial customer experience from a series of manual, disjointed tasks into a streamlined, consistent, and efficient journey. This business process automation example involves using software to handle repetitive steps like collecting documentation, setting up accounts, sending welcome communications, and verifying user information. By doing so, businesses can significantly reduce manual effort, minimize human error, and ensure every new customer receives a timely and professional welcome.
This automation is critical for companies that need to scale rapidly without compromising service quality. For instance, financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase leverage it to reduce account opening times from days to mere minutes. Similarly, e-commerce giants like Stripe and Shopify onboard millions and thousands of merchants, respectively, by automating identity verification, bank account linking, and store setup processes.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating onboarding is not just about efficiency; it is a strategic move to improve customer retention from day one. A smooth, fast, and transparent process sets a positive tone for the entire customer relationship.
Key Strategic Point: The primary goal of onboarding automation is to reduce time-to-value for the customer. The faster they can successfully use your product or service, the more likely they are to become long-term, loyal advocates.
Actionable Insights:
- Start Small, Scale Smart: Begin by mapping your current onboarding journey. Identify the most time-consuming, repetitive tasks, like sending welcome emails or verifying documents, and automate those first.
- Maintain a Human Touch: For high-value or complex accounts, use automation to handle the administrative work but trigger a task for a human success manager to make a personal welcome call.
- Implement Fallbacks: Always have a plan for edge cases. If an automated ID verification fails, the system should automatically create a ticket for manual review to prevent customer frustration.
The following infographic illustrates a typical automated onboarding workflow, breaking down the core stages from initial data collection to full integration.
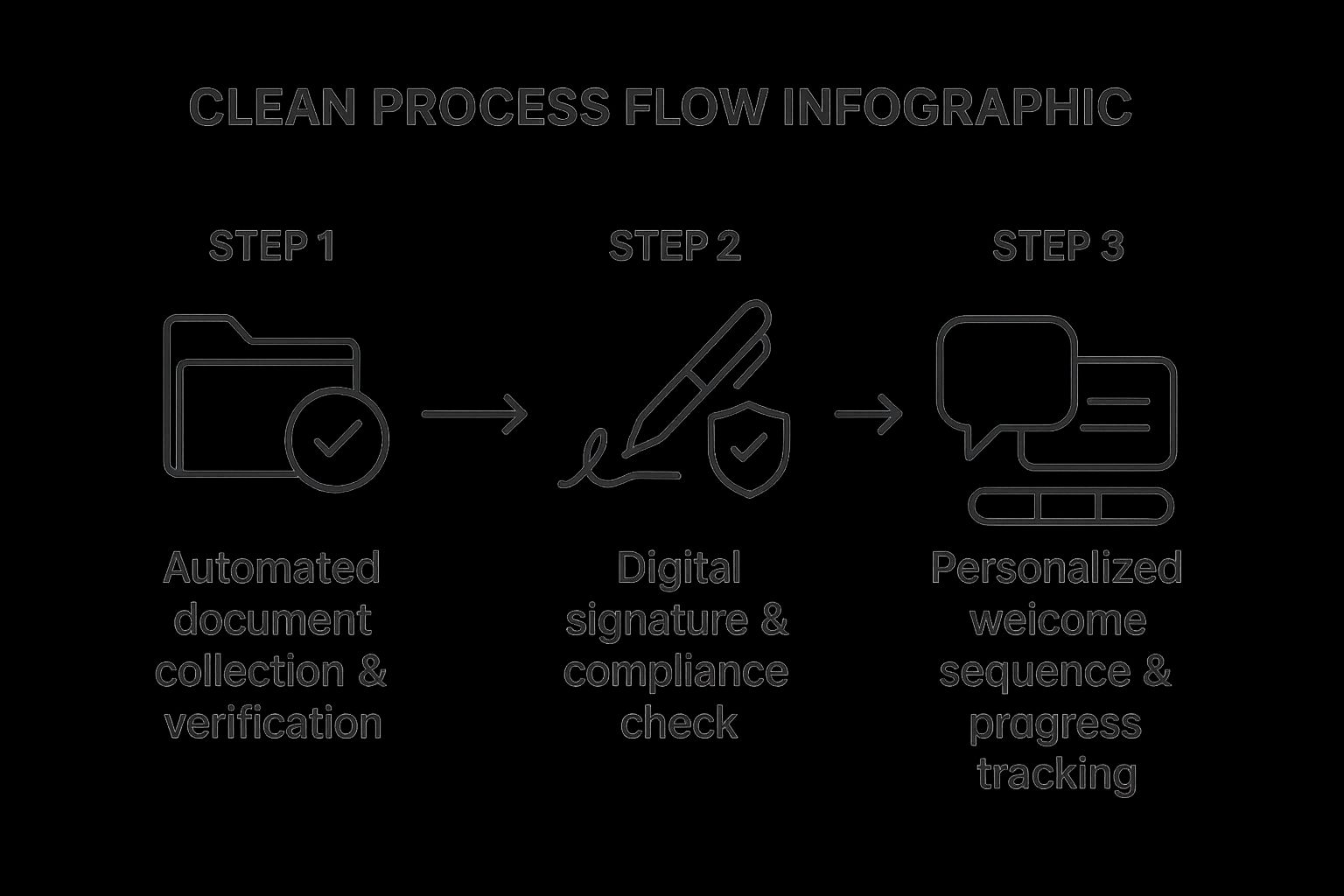
This process flow highlights how automation creates a seamless, secure, and engaging journey by linking critical verification, compliance, and communication steps in a logical sequence.
2. Invoice Processing and Accounts Payable Automation
Invoice processing and Accounts Payable (AP) automation overhaul one of the most labor-intensive financial processes in any business. This business process automation example leverages tools like Optical Character Recognition (OCR), machine learning, and workflow engines to digitize and streamline the entire invoice lifecycle. The system automatically captures invoice data, validates it against purchase orders, routes it for approval, and schedules payment, drastically reducing manual data entry and human error.

This level of efficiency is a game-changer for large enterprises managing massive invoice volumes. For instance, Siemens processes over a million invoices annually with 95% automation, and shipping giant Maersk achieved 85% straight-through processing. These systems, popularized by platforms like SAP and Oracle, not only accelerate processing times but also provide real-time visibility into cash flow and liabilities, empowering CFOs with better financial control.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating AP is more than a cost-saving measure; it’s a strategic initiative to enhance financial accuracy, improve supplier relationships, and strengthen internal controls. By eliminating manual bottlenecks, companies can avoid late payment penalties and even capture early payment discounts.
Key Strategic Point: The core objective of AP automation is to transform the finance function from a transactional cost center into a strategic business partner by freeing up resources for higher-value analysis and financial planning.
Actionable Insights:
- Standardize and Start Small: Begin by standardizing invoice submission formats with your highest-volume suppliers. Focus on automating these predictable, low-complexity invoices first to prove the concept and build momentum.
- Prioritize Exception Handling: A robust automation system is defined by how well it handles exceptions. Design clear workflows for when data doesn’t match or an invoice requires manual review, ensuring no invoice gets lost.
- Focus on Change Management: Prepare your AP team for the shift in their roles. Automation handles the data entry, allowing them to focus on vendor management, exception resolution, and financial analysis. Provide training and clear communication to ensure a smooth transition.
3. Email Marketing Automation
Email marketing automation is a powerful business process automation example that uses trigger-based rules to send personalized emails to subscribers. This technology moves beyond simple email blasts, enabling businesses to deliver timely, relevant content based on customer behaviors, preferences, and lifecycle stages. It automates lead nurturing, customer retention, and targeted sales campaigns, all without direct manual intervention for each send.
This automation is fundamental for scaling customer communication effectively. For instance, Amazon’s famed recommendation engine, which powers its automated emails, is credited with generating a significant portion of its e-commerce revenue. Similarly, Spotify’s “Discover Weekly” emails, automatically curated for each user, achieve exceptionally high open rates, while Airbnb uses automated sequences for booking confirmations, pre-stay reminders, and post-stay review requests to ensure a seamless guest experience.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating email marketing is not just about sending more emails; it is a strategy to build a continuous, personalized dialogue with your audience at scale. A well-executed automated campaign makes customers feel understood and valued, which directly impacts loyalty and conversions.
Key Strategic Point: The primary goal of email automation is to deliver the right message to the right person at the right time. This hyper-relevance transforms email from a broadcast channel into a powerful one-to-one relationship-building tool.
Actionable Insights:
- Start with High-Impact Flows: Begin by automating the most critical touchpoints. Implement a welcome series for new subscribers and an abandoned cart sequence for e-commerce, as these consistently deliver the highest ROI.
- Segment for Precision: Do not send the same message to everyone. Use behavioral data (e.g., pages visited, past purchases) and demographic information to create dynamic audience segments for more targeted campaigns.
- Test and Optimize Relentlessly: Continuously A/B test elements like subject lines, send times, and call-to-action buttons. Use the data to refine your sequences and maximize engagement.
The following image illustrates how behavioral triggers can initiate different automated email sequences, creating a personalized journey for each user.

This workflow demonstrates how you can effectively scale personalized communication, a core principle detailed in many guides. You can learn more about crafting these strategies in resources focused on Email Marketing Automation.
4. HR Recruitment and Hiring Automation
HR recruitment automation overhauls the hiring lifecycle, converting a traditionally manual, lengthy process into a data-driven, efficient workflow. This business process automation example involves deploying technology to manage everything from job posting and resume screening to interview scheduling and offer letter generation. By doing so, organizations drastically reduce time-to-hire, improve the quality of candidates, and deliver a consistent, professional experience to every applicant.
This automation is indispensable for companies managing high-volume recruitment or those in competitive talent markets. For instance, consumer goods giant Unilever utilizes an AI-powered system to assess nearly 2 million applicants annually, freeing up human recruiters for strategic tasks. Similarly, Hilton leveraged automation to slash its average hiring time from 42 days down to just 5, demonstrating the immense impact on operational speed and efficiency.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating recruitment is not merely about speed; it’s a strategic imperative to secure top talent before competitors do. A fast, transparent, and engaging hiring process enhances the employer brand and attracts higher-caliber candidates who value efficiency and communication.
Key Strategic Point: The primary goal of recruitment automation is to reduce time-to-fill while elevating the candidate experience. A positive, streamlined process leaves a lasting impression, even on unsuccessful applicants, building a strong talent pipeline for the future.
Actionable Insights:
- Define Clear Screening Criteria: Before automating, precisely define the skills, experience, and keywords for each role. This ensures AI screeners accurately identify the most qualified candidates, minimizing false positives.
- Maintain Human Oversight: Use automation for initial screening and scheduling, but ensure human recruiters make final interview and hiring decisions. This retains nuance, cultural fit assessment, and critical judgment.
- Audit for Bias: Regularly review your automated tools and their outcomes to ensure they are not inadvertently filtering out diverse candidates. Adjust algorithms and criteria to promote fair and equitable hiring practices.
5. Inventory Management Automation
Inventory management automation revolutionizes how businesses handle stock by using real-time data, predictive analytics, and automated systems to maintain optimal inventory levels. This business process automation example involves software that continuously monitors stock across warehouses and sales channels, automatically triggering reorder alerts or even purchase orders when levels fall below preset thresholds. This prevents costly stockouts, reduces carrying costs, and minimizes manual intervention in procurement.
This automation is essential for retail and e-commerce businesses managing vast and complex product catalogs. For example, Walmart’s sophisticated system tracks millions of items across its stores, using data to forecast demand and automate replenishment. Similarly, fast-fashion giant Zara leverages RFID technology to get real-time inventory visibility, enabling its famous two-week design-to-shelf cycle. Amazon’s anticipatory shipping patents even reveal plans to pre-position inventory in local hubs based on predictive models, a testament to the power of inventory automation.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating inventory management goes beyond just preventing stockouts; it is a strategic initiative to optimize cash flow and improve supply chain resilience. Accurate, real-time data allows businesses to operate leaner, freeing up capital that would otherwise be tied up in excess inventory.
Key Strategic Point: The ultimate objective of inventory automation is to achieve a perfect balance between supply and demand, ensuring product availability while minimizing the financial burden of holding stock.
Actionable Insights:
- Prioritize High-Impact Items: Start by automating inventory management for your fastest-moving or highest-value products (A-items). This delivers the most significant initial ROI and allows you to refine processes before a full-scale rollout.
- Establish a Data Foundation: Accurate automation relies on accurate data. Before implementing any system, conduct a thorough physical inventory count to establish a clean baseline. Integrate this with sales and procurement data for a holistic view. Many companies use integrated platforms for this; you can learn more about Odoo ERP software for inventory management.
- Set Dynamic Thresholds: Don’t use static reorder points. Your system should allow for dynamic thresholds that account for seasonality, promotional spikes, and market trends to prevent both overstock and understock situations.
6. Lead Qualification and Scoring Automation
Lead qualification and scoring automation systematically evaluates and prioritizes potential customers based on their characteristics and behaviors. This business process automation example uses software to track engagement, analyze demographic data, and apply a scoring model to rank leads. The system automatically identifies high-potential prospects, ensuring the sales team focuses its energy on leads most likely to convert, dramatically improving efficiency and closing rates.
This automation is invaluable for businesses with high lead volume, where manual review is impossible. For instance, marketing automation leader Marketo helped its client Punchh achieve a 240% increase in sales-qualified leads by implementing a sophisticated scoring system. Similarly, Salesforce’s Einstein Lead Scoring, powered by AI, has demonstrated a 20% improvement in conversion rates by predicting which leads have the highest probability of becoming customers, allowing sales reps to prioritize their outreach effectively.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating lead scoring is a strategic imperative to bridge the gap between marketing and sales. It creates a data-driven, objective system for lead handoff, eliminating subjective guesswork and ensuring both teams are aligned on what constitutes a “qualified” lead.
Key Strategic Point: The primary objective of lead scoring automation is to maximize the efficiency of your sales pipeline. By focusing human effort on the most engaged and best-fit leads, you increase conversion velocity and revenue.
Actionable Insights:
- Define Criteria Collaboratively: Sit down with both sales and marketing teams to define your ideal customer profile and the specific actions (e.g., pricing page visit, demo request) that indicate buying intent.
- Use Explicit and Implicit Data: Score leads based on both explicit information they provide (company size, job title) and implicit behavioral data (website pages visited, emails opened).
- Review and Refine Regularly: Your scoring model is not static. Analyze which scores lead to closed-won deals and adjust your scoring thresholds and criteria quarterly to improve predictive accuracy.
7. Customer Support Ticket Automation
Customer support ticket automation streamlines help desk operations by automatically categorizing, prioritizing, and routing support requests to the most appropriate agents or departments. This business process automation example uses technologies like natural language processing (NLP) to interpret ticket content, enabling systems to handle repetitive inquiries, escalate urgent issues, and assign complex problems to specialized teams without manual intervention. This frees up human agents to focus on high-value, nuanced customer interactions.
This automation is a cornerstone for modern customer service teams facing high volumes of requests. For example, Zendesk’s Answer Bot can resolve a significant portion of common tickets automatically, while Freshworks’ Freddy AI often handles the initial triage for over half of all incoming customer inquiries. Similarly, ServiceNow’s virtual agent effectively resolves a high percentage of routine IT requests, such as password resets, showcasing the power of automation in delivering immediate solutions.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating support ticketing is not merely about closing tickets faster; it’s about strategically allocating your most valuable resource: your support agents’ expertise. By filtering out repetitive, low-level queries, you empower agents to solve complex problems that genuinely require a human touch, boosting both morale and customer satisfaction.
Key Strategic Point: The primary goal of ticket automation is to increase support capacity and improve resolution quality simultaneously. It allows you to serve more customers with greater accuracy and speed, directly impacting customer loyalty.
Actionable Insights:
- Categorize and Conquer: Start by identifying your most frequent support topics. Create clear, rule-based workflows to automatically tag and route these common issues, like billing questions or feature requests, before layering on more complex AI.
- Create Seamless Escalation: Ensure customers never feel trapped by automation. Provide an obvious and easy way to “speak to a human” at any point in the automated process. The system should then transfer the full context to the agent.
- Leverage CRM Integration: Enhance your ticketing system by connecting it to your CRM. An integrated platform provides agents with a complete customer history, allowing for more personalized and effective support. To get the most out of this, you can learn more about using a CRM for effective customer relationships.
8. Financial Reporting and Analytics Automation
Financial reporting automation streamlines the complex and error-prone process of gathering, consolidating, and presenting financial data. This business process automation example involves using specialized software to connect to disparate data sources like ERPs, CRMs, and spreadsheets. The system then automatically aggregates information, performs calculations, and generates standardized reports such as P&L statements, balance sheets, and cash flow analyses without manual intervention. This ensures accuracy, compliance, and timeliness, freeing finance teams from tedious data wrangling.
This automation is pivotal for organizations that require real-time financial visibility to make agile decisions. For instance, Microsoft famously leveraged automation to slash its financial close process from ten days down to just three. Similarly, Procter & Gamble automated over 90% of its routine financial reporting tasks, allowing its finance professionals to focus on strategic analysis rather than report creation. Marriott International also uses automation to streamline complex financial reporting across its vast network of over 7,000 properties.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating financial reporting is more than a time-saving measure; it transforms the finance function from a historical record-keeper into a forward-looking strategic partner. It provides leaders with immediate, reliable insights needed for forecasting, budgeting, and performance management.
Key Strategic Point: The core objective of financial reporting automation is to accelerate the data-to-decision cycle. By delivering real-time, accurate insights, it empowers leadership to act on opportunities and mitigate risks faster.
Actionable Insights:
- Standardize First, Customize Later: Begin by automating standard, high-volume reports like monthly P&L or sales performance dashboards. Once the core system is stable, you can move on to more complex, custom analyses.
- Prioritize Data Integrity: Before automating, ensure your source data is clean, consistent, and well-governed. Automation is only as reliable as the data it processes; garbage in, garbage out.
- Implement Robust Controls: Establish clear approval workflows and access controls within the automation platform. This ensures that sensitive financial data is secure and reports are validated by the appropriate personnel before distribution.
9. Social Media Management Automation
Social media management automation streamlines content scheduling, publishing, monitoring, and engagement across multiple platforms. This business process automation example involves using software like Hootsuite or Sprout Social to schedule posts in advance, curate relevant content, and manage audience interactions. It allows brands to maintain a consistent, active presence and engage with their community without requiring constant, real-time manual effort from a social media manager.
This automation is invaluable for global brands managing numerous regional accounts. For example, National Geographic automates scheduling to optimize post timing across its 12 main social platforms, reaching diverse audiences effectively. Similarly, Starbucks automates initial customer service responses on Twitter, resolving common queries instantly and freeing up human agents to handle more complex issues. This approach ensures brand consistency and responsiveness at scale.
Strategic Analysis & Actionable Takeaways
Automating social media is not about replacing human interaction; it is about creating the capacity for more meaningful engagement. By handling the repetitive, logistical tasks, it allows marketing teams to focus on strategy, creative content, and authentic community building.
Key Strategic Point: The primary goal of social media automation is to achieve consistency and scale. A well-oiled automated system ensures your brand remains visible and responsive, even outside of active working hours, which is crucial for building a global audience.
Actionable Insights:
- Create Content Buckets: Categorize your content (e.g., educational posts, company news, user-generated content) and use automation to schedule a balanced mix. This prevents your feed from becoming monotonous.
- Automate First-Level Responses: Use tools to automatically respond to common questions or mentions with predefined templates. However, ensure these triggers flag conversations for a human to review and provide a more personalized follow-up.
- Balance Automation with Authenticity: Schedule your core content, but leave room for spontaneous, real-time posts. Use automation to manage your content calendar, not to fake genuine engagement. Human oversight is essential to maintain brand voice.
Business Process Automation: 9 Key Examples Compared
| Automation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Onboarding Automation | High initial setup, multi-system integrations needed | Medium to high, involves compliance & IT resources | 60-80% reduction in onboarding time, improved compliance | New customer acquisition and compliance-heavy sectors | Ensures regulatory compliance, consistent experience, reduces manual errors |
| Invoice Processing & Accounts Payable Automation | Significant configuration and ERP integration | High, requires OCR tech and finance team involvement | 70-90% faster processing, 60-80% cost reduction | High-volume invoice processing in finance departments | Reduces errors, improves vendor relations, enhances cash flow visibility |
| Email Marketing Automation | Moderate complexity, needs quality data and content | Medium, marketing and analytics teams | 320% increase in email revenue, 80% less manual effort | Lead nurturing, customer retention, and conversion | Scalable personalization, detailed insights, 24/7 engagement |
| HR Recruitment and Hiring Automation | Moderate to high, AI integration and monitoring required | Medium, HR and AI specialists | 50-70% reduction time-to-hire, improved candidate quality | High-volume recruiting and talent screening | Data-driven hiring insights, reduces bias, enhances candidate experience |
| Inventory Management Automation | High complexity; multi-location integration | High, IT and operations resources | 20-30% cost reduction, 99%+ inventory accuracy | Retail, manufacturing, supply chain management | Optimizes stock, reduces stockouts, improves demand planning |
| Lead Qualification and Scoring Automation | Complex initial setup, needs historical data | Medium, sales and marketing collaboration | 50-70% more qualified leads, 30-40% higher conversion | B2B sales teams, marketing qualified lead generation | Increases ROI, prioritizes high-value leads, improves sales focus |
| Customer Support Ticket Automation | Moderate setup, ongoing training and rule updates needed | Medium, support teams and NLP expertise | 60-80% faster first response, 40-50% better agent productivity | Customer service centers, help desks | 24/7 responsiveness, consistency, reduces errors |
| Financial Reporting and Analytics Automation | High setup & integration effort | High, finance & IT expertise | 75-90% time saved on reports, real-time visibility | Corporate finance, audit, and compliance | Improves accuracy, speeds closing, enhances compliance |
| Social Media Management Automation | Moderate complexity, requires monitoring and updates | Medium, marketing and social media teams | 70% reduction in management time, 23% engagement increase | Brand management, multi-platform social campaigns | Consistent posting, 24/7 monitoring, scalable engagement |
From Examples to Action: Your Next Steps in Business Process Automation
We’ve journeyed through a diverse landscape of business process automation examples, revealing how smart automation is transforming core operations across industries. From the meticulous precision of automated invoice processing in finance to the strategic efficiency of AI-powered lead scoring in sales, a powerful, unifying theme has emerged. Strategic automation isn’t about eliminating jobs; it’s about elevating them. It’s a force multiplier that liberates your team from the friction of repetitive, manual tasks.
This liberation creates the necessary bandwidth for what truly drives growth: deep strategic thinking, creative problem-solving, and building meaningful customer relationships. The actionable takeaways from our examples show that success lies in a methodical, phased implementation. You don’t need to automate everything at once. The most effective strategies begin by pinpointing the most acute operational pain points.
Distilling the Core Strategy
To translate these business process automation examples into a practical roadmap, focus on these foundational principles:
- Identify High-Friction Processes: Where do bottlenecks consistently appear? Which tasks are most prone to human error? Where is your team spending valuable time on low-impact, repetitive work? Start your automation journey here for the quickest and most significant ROI.
- Start Small, Scale Smart: Select a single, well-defined process to automate first. This could be streamlining customer support ticket routing or setting up automated social media scheduling. A successful pilot project builds momentum and provides crucial learnings for future, more complex integrations.
- Integrate, Don’t Isolate: The most powerful automation connects disparate systems. As we saw with inventory management and financial reporting, linking your tools (like an ERP and your e-commerce platform) creates a single source of truth, eliminating data silos and enabling smarter, data-driven decisions.
Your Path Forward: From Insight to Implementation
Mastering these concepts is no longer a competitive advantage; it’s a fundamental requirement for sustainable growth and operational resilience. By strategically applying the lessons from these business process automation examples, you empower your organization to become more agile, efficient, and customer-centric. The key is to move from passive learning to active implementation.
Begin by auditing your current workflows with your team. Map out a specific process, identify every manual touchpoint, and calculate the time spent. This simple exercise will illuminate the most compelling opportunities for automation. Whether your first step is adopting a CRM with built-in marketing automation or exploring a custom solution to unify your operations, the journey toward a more efficient future begins with that single, decisive action.
Ready to turn these examples into your reality? The experts at KP Infotech specialize in analyzing unique business workflows and engineering custom web, mobile, and ERP solutions that drive measurable results through automation. Let us help you build a tailored strategy that transforms your operational challenges into competitive strengths.
