Optimizing your cloud computing isn't just a technical tweak; it's a strategic approach to managing your resources to boost efficiency, slash costs, and seriously improve performance. Think of it as a continuous cycle of rightsizing, automating, and securing your infrastructure to make sure it's perfectly aligned with what your business actually needs. This is about moving beyond just being on the cloud and making the cloud work smarter for you.
Your Blueprint for Cloud Optimization
Simply migrating your operations to the cloud is just the first step on a much longer journey. The real value starts to show when you stop thinking in terms of a simple "lift and shift" and start building a proactive strategy focused on constant improvement. This guide is your high-level map for navigating the unique challenges and opportunities businesses face in Russia's dynamic market.
The move to cloud services has picked up incredible speed. In fact, the Russian cloud services market saw a massive 36.3% year-over-year growth, ballooning to a size of ₽165.6 billion. This surge points to a growing hunger for domestic cloud solutions and a rapid expansion of local data centre infrastructure. You can dive deeper into this trend and its economic drivers in the full report from Tadviser). With this kind of growth, a solid optimization plan is more critical than ever.
The Four Pillars of an Effective Strategy
A truly successful approach to cloud optimization is built on four core pillars. While each one tackles a different part of your cloud environment, they all work together to give you a powerful competitive edge. Getting a handle on these pillars is the first step before we get into the practical, hands-on actions later.
To give you a quick overview, here's how these four areas break down and what they aim to achieve for your business.
Key Pillars of Cloud Optimization
| Optimization Pillar | Primary Goal | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Management | Achieve financial transparency and eliminate wasteful spending. | Monitoring usage, setting budgets, rightsizing resources, using reserved instances. |
| Performance Tuning | Ensure applications are fast, reliable, and highly available. | Autoscaling, load balancing, choosing correct instance types, optimising databases. |
| Security & Compliance | Protect data and infrastructure while meeting regulatory demands. | Identity and access management, data encryption, compliance audits, threat detection. |
| Automation | Reduce manual effort, minimise errors, and increase operational speed. | Infrastructure as Code (IaC), CI/CD pipelines, automated backups and recovery. |
Let's break down what each of these really means in practice.
Cost Management
This is all about financial governance and cutting out the waste. The goal here is to get a crystal-clear view of your spending, assign costs where they belong, and make absolutely sure you're only paying for the resources you genuinely need.
Performance Tuning
With performance, the main objective is to keep your applications responsive, dependable, and efficient. This involves everything from rightsizing instances and picking the right storage tiers to setting up auto-scaling so you can handle demand spikes without a hitch.
Security and Compliance
A secure cloud is simply non-negotiable. This pillar covers the whole spectrum, from managing who has access and encrypting your data to ensuring you comply with local data sovereignty laws—a major consideration for any business operating in Russia.
Automation
Doing things by hand is slow, full of potential for errors, and just doesn't scale. Automation is where you use powerful tools like Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and CI/CD pipelines to build a cloud operation that is resilient, efficient, and can practically manage itself.
By mastering these four areas, you move beyond just using the cloud to truly commanding it. It’s the difference between having a simple online presence and operating a high-performance digital engine that drives business growth.
Ultimately, a well-thought-out strategy for optimising your cloud is fundamental to your success. If you're just starting out on this path, understanding the initial steps is absolutely crucial. Take a look at our comprehensive guide on the essentials of migration to cloud computing to build a solid foundation for all your optimisation efforts.
Mastering Your Cloud Finances with FinOps
When your cloud bill shows up, it shouldn't be a source of dread. Those unexpected spending spikes are a common headache, but they're entirely preventable with a disciplined approach to financial operations, better known as FinOps. This isn't just about setting a budget and crossing your fingers; it’s about creating a culture of financial accountability for every cloud resource you use—a practice that's especially critical in the Russian market.
Let's get past basic budgeting and talk about real strategies for getting your cloud costs under control. It all starts with total visibility. Without it, you’re just flying blind.
Making Every Ruble Count with Granular Tagging
You can't manage what you can't measure. It's an old saying, but it’s the absolute foundation of effective cloud cost management. A comprehensive tagging strategy is where it all begins. By assigning specific tags to every single resource—think virtual machines, storage buckets, and databases—you can finally see exactly which project, team, or application is responsible for each line item on your bill.
Picture this: a development team spins up a powerful server for a short-term project but forgets to shut it down. Without tags, that cost just gets buried in the massive overall infrastructure bill. But with tags like project:alpha-launch or owner:dev-team, you can immediately pinpoint the source of the expense and take action. That kind of transparency is what builds a true culture of ownership.
Securing Discounts with Strategic Commitments
Cloud providers love to reward commitment. Instead of paying the full on-demand price for your stable, long-running workloads, you can lock in some pretty significant discounts. Local providers like Yandex.Cloud and Selectel have great options for this.
- Reserved Instances (RIs): This is where you commit to using a specific instance type in a certain region for a one or three-year term. In return, you get a hefty discount. It's the perfect move for predictable workloads, like a core application database that hums along 24/7.
- Savings Plans: These offer a bit more flexibility. You commit to a certain amount of hourly spend for a term, and that discounted rate applies across different instance types and even regions. This is a great fit if your usage is consistent but spread across a variety of services.
The trick is to actually look at your usage patterns. Find that baseline level of computing you need all the time and cover it with reservations. This one simple move can often slash the costs for those resources by up to 70%.
Hunting Down and Eliminating Cloud Waste
Cloud waste is the silent killer of IT budgets. It’s the slow, steady bleed from unused or underutilised resources that you're still paying for month after month. Actively hunting down this waste is one of the fastest ways to see a real drop in your spending.
A frequent culprit is the "orphaned" storage volume. This happens when someone terminates a virtual machine but forgets to delete the storage disk that was attached to it. You end up paying for storage that isn't connected to anything. Another classic is leaving development and staging environments running overnight and on weekends, burning through resources for no good reason.
A simple automated script to shut down non-production environments outside of business hours is a low-effort, high-impact win. A server that costs ₽5,000 per month can easily be trimmed down to less than ₽1,500 just by turning it off when nobody is using it.
This isn't a one-time fix; it’s a continuous effort. Regular audits and automated alerts are your best friends here, helping you keep waste to an absolute minimum.
The image below shows how autoscaling dynamically adjusts resources to match demand, which is a core concept in preventing the waste that comes from over-provisioning.
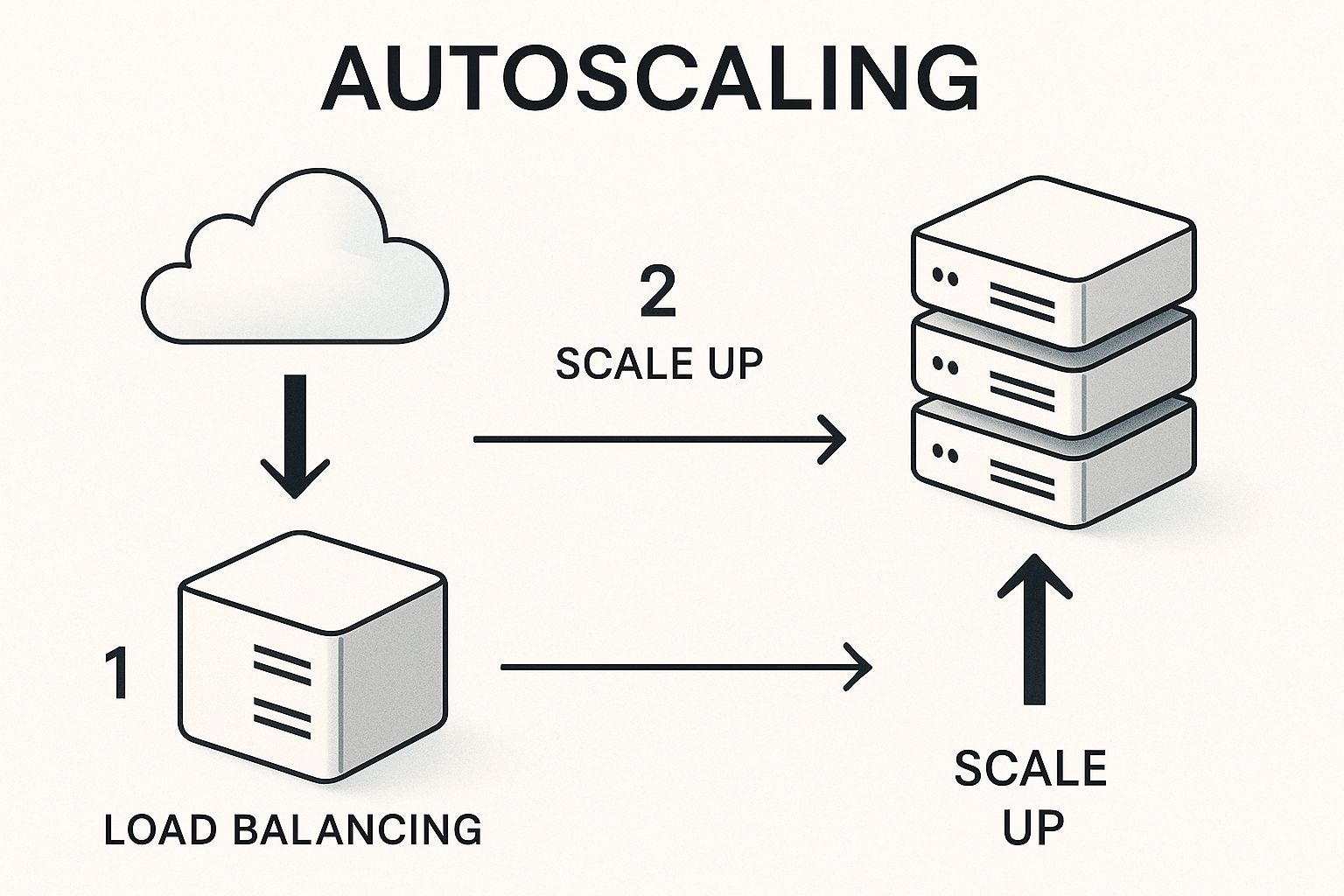
This visual makes it clear: an optimised system automatically adds resources when traffic spikes and removes them during quiet periods, making sure you only pay for what you actually use.
The appetite for these kinds of scalable, cost-effective solutions is growing fast. Projections show Russia's public cloud market is on a path to hit roughly USD 4.62 billion by 2025, fuelled by a strong demand for SaaS and infrastructure services. Given the constant economic pressure on IT budgets, businesses are laser-focused on optimising their workloads with smart orchestration to keep costs down while performance stays high.
If you want to take your cloud financial management to the next level, looking into leveraging AI and automation in FinOps is a powerful next step. It's where you start streamlining data management to get even better business insights and find cost-saving opportunities.
Tuning Cloud Performance for Peak Efficiency
Getting peak performance from your cloud setup isn't about throwing more money at bigger servers. Not even close. Real efficiency comes from a smarter, more deliberate approach: using the right resources, in the right amount, at precisely the right time. This is where performance tuning stops being a technical chore and becomes a massive strategic advantage, making your applications fast, reliable, and surprisingly cost-effective.
It's time to break the old habit of overprovisioning "just in case." A key part of optimising your cloud computing is about being precise and responsive. Let's dive into how you can fine-tune your environment, moving away from guesswork and towards data-driven decisions that give users a better experience while protecting your budget.
The Art of Right-Sizing Your Instances
One of the most common—and costly—mistakes I see is running a virtual machine (VM) that's way more powerful than the workload actually needs. Right-sizing is simply the practice of looking at your real-world usage data, like CPU and memory consumption, to match your instance sizes to what you're actually using. This one activity is often the quickest way to find significant savings and performance gains.
For example, maybe you've got a web server running on an instance with eight virtual CPUs, but your monitoring tools show it rarely spikes above two. In that scenario, you're paying for capacity that sits idle 90% of the time. By downsizing to a smaller instance, you can slash your costs without a single user noticing a difference. The goal is to find that sweet spot where the resource isn't struggling under load, but it isn't wastefully underutilised either.
The core idea behind right-sizing is simple but powerful: stop paying for what you might need and start paying only for what you actually use. This requires continuous monitoring, because workload demands can and will change over time.
A regular audit of your key performance indicators is a must. Hunt for instances with consistently low CPU usage (think below 20%) or memory utilisation. These are your prime candidates for downsizing, offering immediate financial relief and a leaner, more efficient infrastructure.
Implementing Smart Storage Strategies
Not all data is created equal, and your storage choices should absolutely reflect that. Cloud providers offer a whole menu of storage tiers, each with different performance levels and price tags. Using a high-performance SSD for data that's rarely touched is just as wasteful as using slow, archival storage for a high-traffic database.
A much smarter strategy involves classifying your data based on how often it's accessed and what its performance needs are.
- Hot Data: This is your frequently accessed stuff, like active user profiles or current transaction records. It belongs on high-performance storage like Provisioned IOPS SSDs to guarantee snappy response times.
- Warm Data: Think of less frequently accessed data, like monthly reports or older logs. Standard SSD or general-purpose storage usually hits the right balance between cost and performance here.
- Cold Data: This is archival data you have to keep for compliance but will rarely, if ever, access. Moving this to low-cost archival storage can cut your storage costs by over 80%.
By setting up a data lifecycle policy, you can even automate the process of moving data between these tiers. For example, logs older than 30 days can be automatically shifted from standard storage to a cheaper archival tier, optimising costs without anyone lifting a finger. A clear picture of your data helps build a more effective system, which is something you can visualise much better after creating a solid cloud application architecture diagram.
Leveraging Auto-Scaling for Dynamic Demand
User traffic is rarely a flat line. It ebbs and flows with daily cycles, marketing campaigns, or big seasonal events. Manually scaling your infrastructure up and down to meet these peaks is slow and incredibly inefficient. This is where auto-scaling becomes an absolutely essential tool for optimising cloud computing.
Auto-scaling automatically tweaks the number of active instances in your resource pool based on real-time demand. When traffic surges during peak business hours, it spins up new servers to handle the load, ensuring a smooth and responsive experience for your users. On the flip side, when traffic dies down in the middle of the night, it terminates the unneeded instances so you're not burning cash on idle capacity.
Picture an e-commerce site during a massive holiday sale. With a well-configured auto-scaling group, the platform can seamlessly scale from five web servers to fifty to manage the flood of shoppers, then scale right back down once the sale is over. This elasticity is what ensures high availability during critical moments while keeping costs under control during the quiet times. It's a fundamental part of building a resilient and truly efficient cloud operation.
Bolstering Security and Ensuring Compliance
When you move to the cloud, security isn't just the provider's problem—it's a shared responsibility. While they handle the heavy lifting of securing the underlying infrastructure, you're on the hook for everything you build on top of it. Optimising your cloud environment means weaving strong security and compliance measures into the very fabric of your operations, which is especially critical when dealing with Russia's specific data sovereignty laws.
This isn't just about ticking boxes on a checklist. It's about building a resilient, secure foundation that protects your data, your customers, and your business from a constant barrage of threats. Let's break down the practical steps to lock down your cloud assets and stay on the right side of the law.
Mastering Identity and Access Management
Your first line of defence is always controlling who can access what. This is the core purpose of Identity and Access Management (IAM). Getting IAM wrong is like leaving the front door to your office wide open.
The golden rule here is the principle of least privilege. It’s a simple concept: every user, service, or application should only have the absolute bare-minimum permissions needed to do its job. For example, a monitoring tool that only needs to read performance metrics should never, ever have permission to delete a database. This one practice dramatically shrinks your potential attack surface.
Think of it like this: if an account with limited access gets compromised, the blast radius is tiny. An attacker can't delete what they don't have permission to touch. This is a fundamental building block for a secure cloud posture.
Creating Secure Network Perimeters
You wouldn't plug your company's most sensitive servers directly into the public internet, and the same logic holds true in the cloud. You need to create secure, isolated environments for your applications using a combination of virtual networking tools.
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs): These are your own private, cordoned-off sections of the cloud. A VPC lets you define your own virtual network, control your IP address ranges, and create subnets—just like you would in a traditional data centre.
- Network Security Groups (NSGs): These act as a virtual firewall for your instances, controlling all inbound and outbound traffic. You can set specific rules to allow traffic only from trusted sources on specific ports, which is an effective way to block unauthorised access attempts.
A classic setup is to place your web servers in a public subnet, making them accessible from the internet on port 443 (HTTPS), while tucking your database servers away in a private subnet with no direct internet access. The web servers can talk to the databases, but the outside world can't. This creates a secure, multi-layered architecture that’s much harder to breach.
Protecting Your Data at Every Stage
Data is your most valuable asset, so it needs protection whether it's just sitting there or flying across the network. This all comes down to comprehensive encryption.
Encryption at rest protects your data while it's stored on disks or in databases. Most cloud providers offer managed encryption services that make this incredibly simple to set up. Encryption in transit secures your data as it travels between users and your application, or between services in your cloud environment, usually with protocols like TLS/SSL. Turning on both is non-negotiable.
Beyond encryption, a rock-solid backup and disaster recovery plan is essential. Regular, automated backups of your critical data and configurations ensure you can get back on your feet quickly after a hardware failure, a cyberattack, or even a simple "oops" moment. Just be sure to test your recovery process from time to time to make sure it actually works when you need it most.
A key concept in cloud security is understanding who is responsible for what. The "Shared Responsibility Model" clarifies the division of duties between you (the customer) and the cloud provider. This changes depending on whether you're using Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS).
Here’s a breakdown of how those responsibilities typically stack up.
Cloud Security Responsibility Model
| Security Layer | Customer Responsibility (IaaS) | Customer Responsibility (PaaS) | Cloud Provider Responsibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data & Access | Customer manages all data, access policies, and user permissions. | Customer manages all data, user access, and application-level security. | Securing the physical access to data centres. |
| Application | Customer is responsible for securing the application code and logic. | Customer is responsible for securing the application code and logic. | Manages underlying application platform (for PaaS). |
| Operating System | Customer manages and secures the OS, including patches and updates. | Cloud provider manages the OS and its security. | Manages the OS, virtualisation layer, and patching. |
| Network Controls | Customer configures VPCs, subnets, firewalls, and routing. | Customer configures network security groups for their application. | Manages the physical network and core network services. |
| Physical Hardware | N/A (Handled by provider) | N/A (Handled by provider) | Secures and maintains all servers, storage, and networking hardware. |
Understanding this model is crucial. Assuming the provider is handling a security layer that is actually your responsibility is one of the most common—and dangerous—mistakes a company can make in the cloud.
Navigating Russian Compliance and Data Sovereignty
For any business operating in Russia, complying with data sovereignty laws is a major priority. These regulations often require that the personal data of Russian citizens be stored and processed on servers physically located inside the country. This has a massive impact on your choice of cloud provider.
The Russian cloud computing market is seeing huge demand from sectors like IT, healthcare, and finance, all pushing forward with digital transformation. While global providers have a presence, local players like Yandex.Cloud and Selectel are often the go-to choices precisely because they can guarantee compliance with Russian data protection laws.
You can dig deeper into these market dynamics in the full report. Partnering with a domestic provider that guarantees data residency isn't just about meeting a legal requirement; it's a strategic move that simplifies your compliance journey and builds trust with your local customers.
Automating Operations for Better Scalability
Manual tasks are the single biggest bottleneck to growth in any cloud environment. To get the most out of cloud computing, you have to move away from hands-on, repetitive work and embrace automation. This builds an operation that’s more resilient, efficient, and reliable. It’s not just about saving time; it's about creating systems that scale effortlessly and free your team from mundane chores so they can focus on what really matters: innovation.
Imagine a server failing in the middle of the night. The manual approach is a frantic phone call, a bleary-eyed engineer logging in, and a stressful scramble to launch a replacement. The automated approach? A monitoring system detects the failure, a script automatically terminates the faulty instance, and a new, perfectly configured server takes its place—all before anyone even gets paged. That’s the power we're talking about.
Defining Your World with Infrastructure as Code
The bedrock of modern cloud automation is Infrastructure as Code (IaC). Instead of manually clicking through a web console to configure servers, networks, and databases, you define your entire environment in configuration files. Tools like Terraform and OpenTofu have become the industry standard for this, letting you manage your infrastructure with the same version control and review processes you use for application code.
With IaC, deploying a complete staging environment becomes as simple as running a single command. Need to replicate it for a new region? Just change a few variables and run it again. This makes your deployments repeatable, predictable, and completely free of the human error that always creeps in with manual setups. It turns a complex, multi-day task into a reliable, automated process that takes just minutes.
Think of IaC as the architectural blueprint for your cloud. It’s a single source of truth that describes exactly what your environment should look like, making it incredibly easy to track changes, roll back mistakes, and maintain consistency across all your deployments.
Speeding Up Releases with CI/CD Pipelines
Once your infrastructure is codified, the next logical step is automating your software release process. A Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline automates every step needed to get code from a developer's machine into production. This pipeline handles everything from compiling code and running tests to deploying the finished application.
Here’s a practical look at what a typical pipeline does:
- A developer commits new code to a version control repository like Git.
- This action automatically triggers the CI/CD pipeline.
- The pipeline builds the code and runs a series of automated unit and integration tests to catch bugs early.
- If all tests pass, it packages the application into a container (like Docker).
- Finally, it automatically deploys the new version to your staging or production environment with zero downtime.
This dramatically speeds up your time-to-market. Instead of having one or two big, risky releases a month, you can confidently push small, incremental updates multiple times a day. This approach is a core part of building a modern, agile operation, and you can explore more of these concepts in our detailed guide on the best practices for DevOps.
Creating Self-Healing Systems
The ultimate goal of automation is to create an environment that can manage and heal itself. This involves combining automated monitoring with scripted responses to common problems. When a system can detect an issue and fix it without human intervention, you achieve a whole new level of resilience and reliability.
Consider these real-world scenarios for self-healing:
- Automated Server Replacement: As mentioned, a monitoring tool detects a failed health check on a web server. An automated workflow is triggered to terminate the unhealthy instance and launch a new one from a pre-configured template.
- Dynamic Database Failover: If a primary database instance becomes unresponsive, an automated system can promote a read replica to become the new primary, rerouting traffic to ensure the application remains online.
- Disk Space Management: A script can monitor disk usage on your servers. If a disk starts to fill up, it can automatically trigger a clean-up process to archive old log files, preventing an outage caused by a full disk.
By anticipating common failure points and building automated responses, you move from a reactive "firefighting" model to a proactive, self-managing system. This isn't science fiction; it’s a practical and achievable goal for any team serious about optimising their cloud for the long haul.
Common Questions About Cloud Optimisation
When you start digging into the world of optimising your cloud setup, a lot of questions tend to surface. It's completely normal. The sheer number of options and strategies can feel a bit overwhelming, so we've put together some direct, no-fluff answers to the queries we hear most often.
The goal here is to clear up any confusion and give you the confidence to move forward. Let's tackle these questions head-on.
How Often Should We Review Our Cloud Setup?
This is a fantastic question because it gets right to the heart of what continuous optimisation really means. The short answer? It’s not a one-time project. Your cloud environment needs constant attention, but the intensity of that review can vary.
For a more structured approach, think of it as a rhythm:
- Weekly Checks: This is a quick glance at your main cost and performance dashboards. You're just looking for any sudden spikes or odd behaviour that needs immediate attention.
- Monthly Audits: Time for a deeper dive. This is when you hunt for idle resources, check if your auto-scaling is performing as expected, and make sure your tagging is clean and consistent.
- Quarterly Strategy Sessions: Step back and look at the bigger picture. Are your reserved instances still a good fit for your workload? Is it time to explore newer, more efficient instance types that have been released?
This regular cadence ensures you catch small issues before they snowball into major problems and keeps your cloud strategy perfectly aligned with where the business is headed.
What Is the Biggest Mistake Companies Make?
Without a doubt, the most common and costly mistake is overprovisioning resources "just in case." It's a habit left over from the days of on-premises hardware, where buying bigger servers was the only way to plan for future growth. In the cloud, that mindset is a direct path to wasted money.
The cloud's greatest strength is its elasticity—the ability to scale up and down on demand. Failing to use this feature means you're paying for capacity that sits idle most of the time, completely wiping out one of the main financial benefits of moving to the cloud in the first place.
The fix requires a cultural shift. Instead of guessing at peak demand, use your monitoring and analytics tools to understand your actual usage patterns. Implement auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes dynamically and make right-sizing a continuous, ongoing process, not a one-off task.
Is Moving to a Multi-Cloud Strategy Better?
A multi-cloud strategy—using services from more than one cloud provider—can offer some serious benefits, but it's no silver bullet. It can definitely increase your resilience and help you avoid getting locked into one vendor. This allows you to pick the absolute best service for a specific job, regardless of the provider. For instance, one provider might have a superior machine-learning service, while another offers a more cost-effective database.
However, this approach brings its own set of headaches. Managing different environments, security models, and billing systems requires more specialised skills and much more robust management tools. Before you jump in, you have to carefully weigh the benefits of cherry-picking services against the operational overhead of running multiple platforms. For many businesses, a simpler, single-provider setup is often the more efficient choice.
At KP Infotech, we specialise in helping businesses navigate these complexities to build efficient, scalable, and secure cloud environments. From initial strategy to ongoing management, we provide the expertise you need to truly master your cloud operations. If you're ready to stop guessing and start optimising, explore our tailored digital transformation solutions today.
