So, what’s the real difference? It boils down to this: React is a nimble JavaScript library, perfect for dynamic single-page applications where you need to move fast. Angular is a comprehensive, structured framework built for large-scale enterprise systems where consistency is king.
Your final decision hinges entirely on your project's scale, your team's structure, and what you want to achieve long-term.
Choosing Your Frontend Framework: A Quick Comparison
Picking between Angular and React isn't about which one is "better." It's about finding the tool that clicks with your project's specific needs. Both are powerhouses for building modern UIs, but they're built on fundamentally different philosophies that shape everything from setup to maintenance.
The React Philosophy: Flexibility and Focus
Maintained by Facebook, React is a JavaScript library that does one thing exceptionally well: build user interfaces. This laser focus gives developers a ton of freedom. You get to pick and choose your own libraries for things like routing and state management, letting you build a tech stack that’s perfectly suited to your project.
This à la carte approach makes it a favourite for startups and agile teams who value quick iteration and a component-based architecture that can be easily updated.
The Angular Philosophy: Structure and Stability
On the other side of the fence, you have Angular. Backed by Google, it's a full-blown framework that comes with everything included. It’s an opinionated, all-in-one solution with a powerful command-line interface (CLI), built-in routing, and state management right out of the box.
This integrated ecosystem enforces a consistent structure across large teams and complex projects. That makes it a rock-solid choice for enterprise-level applications where stability and clear architectural patterns are non-negotiable.
The frontend world is always in motion. To keep up with how these tools are evolving, it's worth checking out the latest frontend framework news and trends. Remember, Angular and React are just two of many options. For a broader perspective, a guide on the best web application frameworks can help you see the bigger picture.
Ultimately, your choice will come down to your team’s comfort level with TypeScript versus JavaScript, the sheer complexity of the application you’re building, and how quickly you need to move.
Before we dive deeper, here’s a quick summary to help you see the core differences at a glance.
Angular vs React At a Glance
This table offers a high-level summary of the fundamental differences between the two, providing a quick reference to help frame your decision.
| Criterion | Angular | React |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Comprehensive, opinionated framework | Focused JavaScript library for UI |
| Primary Language | TypeScript (required) | JavaScript (JSX) with optional TypeScript |
| Data Binding | Two-way data binding | One-way data binding |
| Architecture | Full Model-View-Controller (MVC) structure | Component-based, focused on the "View" layer |
| Ecosystem | All-in-one solution with built-in tools | Relies on an external ecosystem for routing, state, etc. |
| Best For | Large enterprise applications, complex systems | Single-page applications (SPAs), reusable components |
Each of these points has a major impact on development workflow, team structure, and long-term maintenance. Now, let’s get into the specifics of what these differences mean in the real world.
Comparing Core Architectural Philosophies
To really get to the heart of the Angular vs React debate, we have to look past the feature lists and dive into their core philosophies. These foundational differences shape everything—from how your developers work and how you structure teams to whether your project will scale gracefully in the long run. They represent two fundamentally different ways of thinking about how to build a modern web application.
Angular arrives on the scene as a complete and opinionated framework. Think of it like a full-service workshop; it comes with every tool you'll need, all neatly integrated, and a clear set of instructions for how to use them. It’s not just a library for building UIs; it’s an entire platform for application development.
This all-in-one approach is built on battle-tested software design patterns like Model-View-Controller (MVC). By providing built-in solutions for routing, state management, and dependency injection right out of the box, Angular hands you a standardised blueprint that keeps large-scale projects consistent and manageable.
The Structured World of Angular
Angular’s integrated structure is its most defining trait. The moment you spin up a new project with the Angular CLI, you’re in its world, operating within its well-defined ecosystem. For big, distributed development teams, this prescribed structure is a massive advantage.
Its key architectural pillars include:
- Built-in Dependency Injection: Angular handles how components get their dependencies automatically, which makes testing a whole lot simpler and encourages modular, reusable code.
- Integrated Routing: The powerful Angular router is a core part of the framework, giving you a consistent way to handle navigation and application views without bolting on another library.
- Consistent Tooling: The Angular CLI is your workhorse. It automates tons of development tasks—from generating components to building and deploying the app—enforcing a uniform workflow for everyone on the team.
This opinionated nature means developers spend less time debating architecture and more time actually building features. The framework's structure ensures that whether your team has five or fifty developers, the codebase maintains a predictable form. For big companies that prize long-term maintainability and stability, this architectural rigour is priceless. It lowers the mental overhead for new developers joining a project because the rules of the road are already set by the framework itself.
The Flexible Ecosystem of React
On the other side of the fence, React is a focused JavaScript library, not a full-blown framework. Its one and only job is to build and render user interface components with incredible efficiency. This minimalist philosophy gives developers immense freedom, but it also puts the responsibility of choosing all the other architectural pieces squarely on their shoulders.
React doesn't ship with a built-in router or a global state management solution. Instead, it leans on a massive, vibrant ecosystem of third-party libraries to fill those gaps. This "bring your own tools" approach lets teams assemble a custom-tailored tech stack that perfectly suits their project’s unique needs.
Some common additions to a React project include:
- Routing: Libraries like React Router have become the de facto standard for managing navigation in single-page applications.
- State Management: For complex apps, you'll almost certainly integrate tools like Redux, MobX, or the more modern Zustand to manage application state beyond individual components.
- Styling: Developers get to pick their poison, choosing between CSS-in-JS solutions like Styled Components, utility-first frameworks like Tailwind CSS, or classic CSS modules.
This modularity is React's greatest strength. It keeps the core library lean and lightning-fast, allowing you to add functionality only as needed and avoid the bloat of unused features. For projects that need to move fast, prototype quickly, or have very specific architectural demands, this flexibility is a huge asset. It empowers developers to pick the absolute best tool for each job, leading to highly optimised and bespoke solutions.
Angular offers a structured blueprint for building your application, while React provides high-performance components and lets you choose the rest of the architecture.
In the end, the choice between Angular's structured framework and React's flexible library boils down to your project's context. A large enterprise system will likely benefit from Angular's consistency, whereas a fast-moving startup may find React's agility and customisability a much better fit.
Performance and DOM Manipulation Differences

When you get into the trenches of the Angular vs React debate, performance is always a hot topic. The conversation usually zeroes in on how each one handles updates to the user interface, and the core of that difference is their approach to the Document Object Model (DOM)—the tree-like map of a webpage. Getting your head around this is the key to knowing how your app will hold up under pressure.
Angular works directly with the real DOM. When something in a component's state changes, Angular goes straight to the source and updates the actual DOM tree. This is a very direct and straightforward process, but it can be computationally expensive. If your application is highly dynamic, with constant and numerous updates, tinkering with the real DOM too often can lead to performance bottlenecks.
React, on the other hand, famously brought the virtual DOM into the mainstream. Think of it as a lightweight, in-memory copy of the real DOM. When a component's state changes, React first builds a new virtual DOM tree and then compares it to the previous version.
This comparison, a process known as "diffing," lets React pinpoint the exact, minimal changes needed. It then batches these updates and applies them to the real DOM in the most efficient way it can, cutting down on direct manipulations. This often leads to snappier UI rendering, especially in applications juggling a lot of data.
Change Detection Mechanisms
Beyond just the DOM, the way each framework figures out when to update is a massive factor in performance. Both have come a long way, but their foundational philosophies are still quite different.
Angular uses a sophisticated change detection system. In older versions, this could be a bit overzealous, checking the entire component tree for changes whether it needed to or not. Modern Angular, however, has introduced much smarter strategies like OnPush change detection. This lets developers tell the framework to only check components when their input properties change, which can massively boost performance.
React's change detection is naturally tied to its state management. When a component's state is updated via setState or a hook like useState, React knows it needs to re-render that component and its children. While this is usually efficient, developers have to be careful to avoid unnecessary re-renders, often reaching for tools like React.memo or the useCallback hook to stop performance from degrading in complex component trees.
While the virtual DOM often gives React an edge in benchmarks for highly dynamic UIs, the performance gap isn't as wide as it once was. For most standard applications, the actual performance is dictated more by developer practices—such as code splitting, lazy loading, and state management strategies—than by the underlying framework itself.
The Impact of Bundle Size
Another real-world performance issue is the initial load time, which is directly tied to the application's bundle size. As a full-blown framework, Angular naturally has a larger initial footprint. Its core libraries and dependencies add up, resulting in a bigger bundle that users have to download on their first visit.
React, being just a library, starts off much leaner. However, its final bundle size is completely dependent on the other libraries you pull in for things like routing and state management. A complex React application can easily end up with a bigger bundle size than a similar Angular app if you're not careful about what you add.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the performance trade-offs:
| Performance Aspect | Angular | React |
|---|---|---|
| DOM Type | Real DOM | Virtual DOM |
| Typical Advantage | More predictable updates in some scenarios. | Faster rendering for data-heavy, dynamic UIs. |
| Change Detection | Zone.js-based, can be optimised with OnPush. | Triggered by state changes, requires memoization. |
| Initial Bundle Size | Larger due to its framework nature. | Smaller core, but grows with dependencies. |
At the end of the day, both frameworks can be used to build incredibly high-performance applications. The right choice in the Angular vs React performance battle often boils down to your specific use case. React's virtual DOM might give you a slight edge for apps with thousands of elements updating in real-time, like a stock ticker. In contrast, Angular's structured and optimised ecosystem can deliver excellent, consistent performance for large-scale enterprise applications where developer practices are standardised.
Data Binding and State Management Explained

How an application handles its data is a massive factor in the Angular vs React debate. The two technologies manage information in fundamentally different ways, and this single choice directly impacts development speed, how painful debugging is, and the entire architecture of your application. The decision you make here really shapes your team's day-to-day work.
Angular is famous for its powerful two-way data binding. This approach creates an automatic, real-time link between the data model and the user interface. When a user types into a form, the underlying data updates instantly, and if the data changes, the form field reflects it immediately. This makes building complex forms much simpler because you don't have to write a bunch of boilerplate code just to keep everything in sync.
React, on the other hand, is a firm believer in one-way data flow. Here, data moves in a single, predictable line: from parent components down to child components. If a child component needs to change something, it sends a signal back up to the parent. The parent updates its own state, and then the new data flows back down the chain.
This one-way street gives you incredible control and makes debugging a whole lot easier. Since you know exactly which direction the data is flowing, tracking down the source of a weird state change is as simple as following the stream back up the component tree. For large, complicated apps, that predictability is a lifesaver.
Managing Application State
The differences go deeper than just binding; they get to the heart of state management. An application's "state" is the complete snapshot of all its data at any given moment. Managing it well is the key to building something that doesn't fall apart under pressure.
Angular hands you an integrated, "batteries-included" solution right out of the box. Its whole architecture is designed to handle complex data using a combination of services and the powerful RxJS library.
- Services: In Angular, services are single instances that can be shared across any component, creating a central hub for storing and managing your application's state.
- RxJS: This is a library for reactive programming that helps you manage asynchronous data streams. It makes it much easier to handle things like API calls, user events, and other tricky data flows.
This built-in system gives developers a standardised way to handle state without having to shop for third-party tools, reinforcing the structured, opinionated nature of the framework.
React’s Ecosystem-Driven Approach
React’s core is intentionally lean, which means it doesn't force a global state management solution on you. For simple components, developers can get by just fine using local state with hooks like useState. But as an application grows, passing state down through many layers of components—a headache known as "prop drilling"—becomes a real pain.
To solve this, the React community has built an incredible ecosystem of powerful state management libraries. This freedom lets teams pick the perfect tool for their specific needs, whether it's the battle-tested Redux, the simpler Zustand, or any number of other great options.
The core trade-off is clear: Angular offers a powerful, built-in system that ensures consistency, while React provides the flexibility to choose the ideal state management tool from a vast and innovative ecosystem.
Ultimately, your project's scale and complexity will decide which approach is a better fit. A massive enterprise application with a large, distributed team might get more value from Angular’s standardised system. In contrast, a fast-moving project that needs a highly customised or lightweight state solution will probably find React’s library-driven flexibility a huge advantage. The Angular vs React decision here is a classic showdown between structure and freedom.
Developer Experience and Job Market Insights
Picking between Angular and React is about more than just technology. It’s a strategic choice that shapes your team’s entire workflow, your hiring pipeline, and even your own career path. The day-to-day experience of a developer and the job market trends for each reveal two very different ecosystems, built for different kinds of projects and professional goals.
The initial journey into either technology really sets the tone for what’s to come. Most developers find React’s learning curve to be a bit gentler. Its focused API and use of JSX—which lets you blend HTML-like syntax right into your JavaScript—feels natural for anyone with a solid JS background. This straightforward entry point means teams can get up and running, building components and seeing results, very quickly.
Angular, on the other hand, asks for a bigger commitment upfront. It's a full-blown framework, so you’re not just learning how to build components. You have to get your head around modules, dependency injection, and TypeScript right from the start. While TypeScript is a huge long-term win for code safety and organisation, it adds another layer of concepts for newcomers to tackle.
Navigating the Learning Curve
React’s core simplicity is a massive draw. Since it’s a library, not a complete framework, developers can learn the essentials—components, state, and props—and start being productive in a surprisingly short amount of time. The complexity in a React project builds gradually as you pull in other libraries for things like routing or state management, which lets the learning happen more organically.
Angular demands more of an initial investment. Mastering its opinionated structure means learning "the Angular way" of doing things from day one.
For development teams, this is the central trade-off: React offers a faster start with more architectural decisions down the road, while Angular requires a greater initial commitment for a more standardised and predictable development process long-term.
This difference in philosophy directly influences where you’re likely to see each technology in the wild. React’s agility and speed-to-market have made it a powerhouse in the startup world and for companies building highly interactive, modern user interfaces. Angular's structured and stable nature has cemented its place in large corporations and enterprise-level applications, where long-term maintainability and team consistency are the top priorities. If you need to bring a skilled professional onto your team for these kinds of dynamic projects, you can learn more about how to hire a React.js developer.
Job Market Demand and Salary Trends
The professional landscape for Angular and React reflects their different use cases, with clear patterns showing up in job demand and compensation. Employment data from major Russian IT job boards and developer surveys throughout 2024 paint a clear picture. React skills are consistently ranked among the top five most requested frontend competencies in Russia’s IT market, showing up in nearly 57% of frontend vacancies posted. In comparison, Angular-specific roles appear in about 20% of job postings.
Salary surveys from the same period show that React developers in Russia earn, on average, 15–20% more than their Angular counterparts. This reflects both the higher demand and the versatility that React expertise brings to the table. For more details, you can explore the Russian frontend job market trends on devsdata.com.
This data really highlights a trend where React’s flexibility is highly valued across a wider range of industries, especially in fast-moving tech hubs.
Ecosystem and Community Support
A technology’s real strength often comes from its community and the ecosystem built around it. Both Angular and React have the backing of tech giants—Google for Angular and Meta for React—but their ecosystems have grown in very different directions.
The React community is famous for its breakneck pace of innovation and a massive ocean of third-party libraries and tools. This creates an environment where you can find a pre-built solution for almost any problem imaginable. The flip side is that it requires developers to constantly stay on top of a shifting landscape of best practices and popular libraries.
Angular's ecosystem is more controlled and consistent. The core Angular team provides and maintains most of the essential tools, making sure everything works together seamlessly. This cuts down on decision fatigue for developers and guarantees a certain level of stability, though it can sometimes mean waiting for official updates instead of grabbing the latest community-driven solution.
Choosing The Right Tool For Your Project
Picking a frontend technology isn't just about comparing features; it's a strategic decision that shapes your entire project's future. The choice between Angular and React has to be driven by the real-world demands of your application, the structure of your team, and your long-term business goals. This is where we move from theory to practice and match the right tool to the job.
This decision tree gives you a simple mental model for choosing between the frameworks, starting with project scale and then drilling down into specific technical needs.
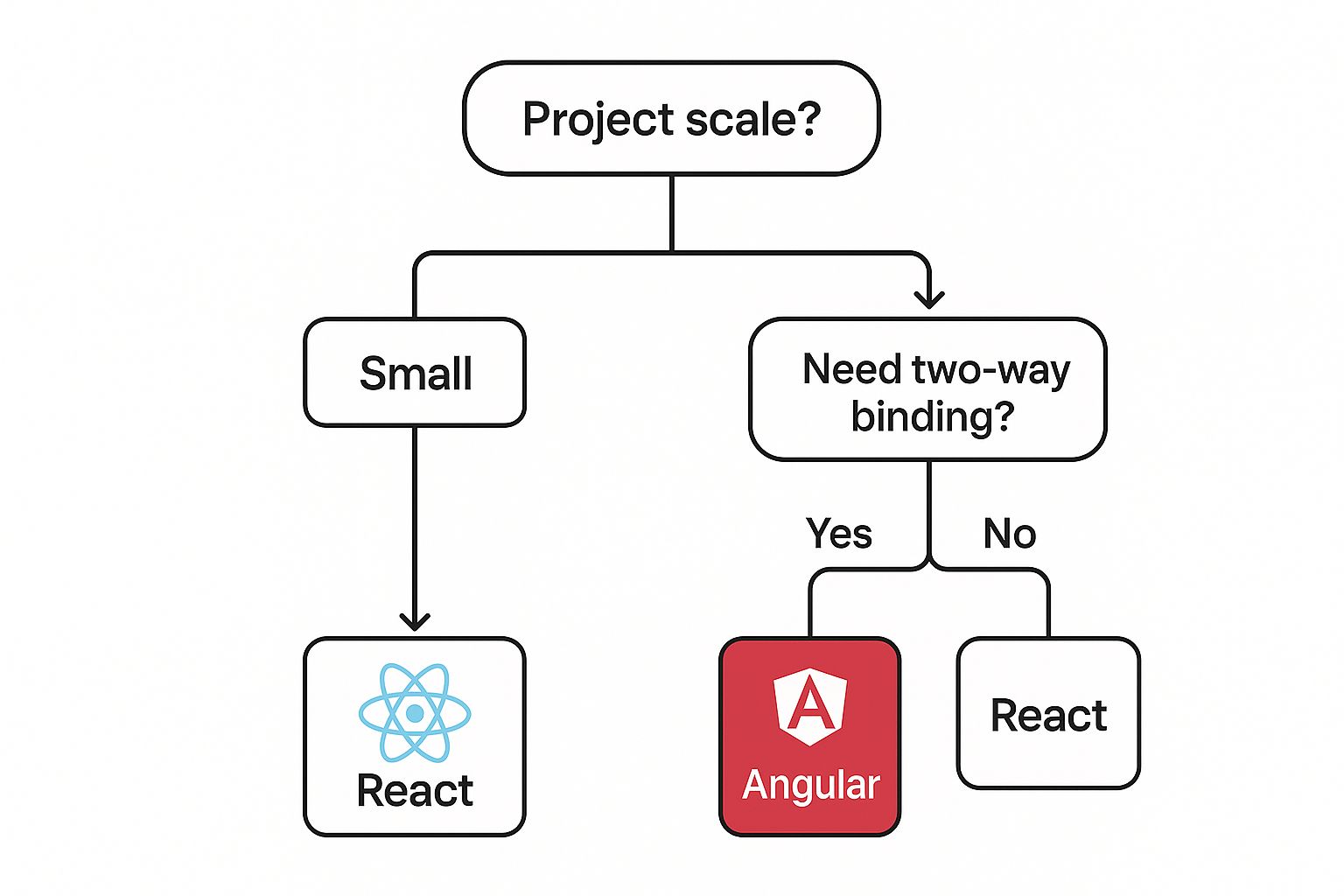
As you can see, while project size is a good first filter, it’s the finer details—like how you need to handle data binding—that often become the deciding factor in more complex applications.
When To Choose Angular For Your Project
Angular’s structured, opinionated nature makes it a powerhouse for specific, demanding scenarios. It truly shines in environments where consistency, structure, and long-term maintenance are non-negotiable. Its all-in-one approach gives you a solid, predictable foundation right from the start.
Consider Angular the clear winner for:
- Large-Scale Enterprise Systems: When you have dozens or even hundreds of developers working on a complex application, Angular's built-in architecture and standardised tools enforce consistency. This rigid structure is a lifesaver for distributed teams, making sure everyone is building the same way.
- Projects Requiring A Stable, Long-Term Maintenance Strategy: The framework’s predictable release cycle and self-contained ecosystem mean fewer dependency headaches down the road. This makes it far easier to manage the application through its entire https://kpinfo.tech/software-development-life-cycle-example/, from the first line of code to ongoing updates years later.
- Complex Web Applications: If you're building something with intricate requirements, like a progressive web app (PWA) or a system needing detailed state management out of the box, Angular's integrated ecosystem is a huge advantage. It comes packed with a powerful CLI and built-in routing, so you don't have to piece things together.
Angular’s core strength is its ability to bring order to chaos. It provides a clear, standardised blueprint that helps large teams build and maintain sophisticated applications efficiently over the long haul.
Its opinionated structure cuts down on "decision fatigue," letting developers focus on building features instead of endlessly debating architecture. This makes it a natural fit for corporate environments where scalability and predictability are key.
When React Is The Ideal Solution
React’s flexibility and laser focus on the UI layer make it a fantastic choice for projects where development speed and dynamic user experiences are the top priorities. Its component-based architecture and massive ecosystem empower teams to build highly customised solutions, and fast.
React is the go-to option for:
- Dynamic Single-Page Applications (SPAs): For things like interactive dashboards, social media feeds, or any app where data is constantly changing, React’s virtual DOM delivers the performance you need for a buttery-smooth user experience.
- Reusable Component Libraries: If your organisation needs to build a design system or a library of UI components to be shared across multiple projects, React’s focused, unopinionated nature makes it the perfect foundation.
- Projects Prioritising Rapid Development And Iteration: Startups and agile teams often lean on React because of its relatively gentle learning curve and the ability to quickly prototype and launch a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). Its enormous ecosystem provides ready-made solutions for almost any problem you can think of.
- Cross-Platform Mobile Development: Through React Native, teams can use their existing web development skills to build truly native mobile apps for both iOS and Android from a single codebase. This can dramatically cut down on development time and cost.
If your project's needs point towards React, bringing in expert React.js development services can ensure you get a robust and efficient build. By aligning the framework’s strengths with your project’s specific demands, you set yourself up for a successful outcome.
Best-Fit Scenarios for Angular and React
To simplify the decision, this table breaks down common project requirements and matches them to the framework that typically handles them best.
| Scenario or Requirement | Recommended Choice | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Large-scale enterprise application with a large, distributed team. | Angular | Its opinionated structure and standardised tooling enforce consistency, which is critical for maintaining code quality and onboarding new developers in a large project. |
| Need for a fast, interactive single-page application (SPA). | React | The virtual DOM is optimised for frequent UI updates, making it ideal for dynamic applications like social media feeds or real-time dashboards where performance is key. |
| Building a reusable UI component library for multiple projects. | React | React's primary focus is on the view layer, making it unopinionated and perfect for creating standalone, reusable UI components that can be dropped into any project. |
| Project requires a stable, all-in-one solution with long-term support. | Angular | As a complete framework backed by Google, Angular provides a predictable ecosystem with integrated solutions for routing, state management, and more, reducing dependency risks. |
| Fast-paced startup environment needing a quick MVP. | React | Its smaller API surface and vast ecosystem of libraries allow for rapid prototyping and iteration, helping teams get a product to market quickly to gather user feedback. |
| Developing native mobile apps for both iOS and Android from one codebase. | React | With React Native, developers can leverage their existing React knowledge to build true native mobile applications, saving significant time and resources. |
Ultimately, the best choice depends entirely on your project's context. Angular provides a robust, comprehensive framework for building complex, scalable applications with a focus on consistency. React offers a flexible, high-performance library perfect for dynamic UIs and rapid development cycles.
Frequently Asked Questions About Angular and React
When you're this deep into the Angular vs. React debate, a few key questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most common ones to help you nail down your final decision.
Which Is Better for SEO?
Both frameworks can deliver top-tier Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), but they take different roads to get there. The magic ingredient is server-side rendering (SSR), which hands search engine crawlers a fully-rendered page they can index in a heartbeat.
Angular has this covered with Angular Universal, a core module designed specifically to pre-render pages on the server. With React, you lean on its incredible ecosystem, using battle-tested frameworks like Next.js or Gatsby to handle SSR for you.
Ultimately, both approaches work flawlessly. SEO success here is all about how you implement it, not a built-in limitation of either technology.
Can I Use TypeScript with React?
You absolutely can, and you absolutely should. While TypeScript is a non-negotiable part of Angular, it’s an optional—but highly recommended—superpower for React projects.
Adding TypeScript to your React codebase brings strict type safety, which is a lifesaver for catching bugs before they ever make it to production. It drastically improves your code quality and makes scaling large applications a much cleaner, more manageable process. Modern tooling like Create React App even supports it right out of the box.
The real question isn’t if you can use TypeScript with React, but why on earth you wouldn’t. The stability and error-reduction it offers have made it the standard for any serious React development.
Which Has a Better Mobile Development Solution?
When it comes to building for mobile, React has a clear and powerful advantage: React Native.
React Native isn't just a web app in a mobile wrapper. It allows you to build genuinely native mobile applications for both iOS and Android from a single JavaScript codebase. It renders real native UI components, which delivers the kind of slick performance and user experience that feels completely at home on the device—often indistinguishable from an app built in Swift or Kotlin.
Angular’s route to mobile usually involves frameworks like Ionic, which wrap your web application inside a native shell. While this hybrid approach is effective and gets the job done, it can sometimes lack the true native feel and peak performance that React Native delivers, giving React the undeniable edge for any mobile-first project.
