The fundamental difference between React and AngularJS boils down to a simple concept: React is a specialised JavaScript library for building user interfaces, focusing on speed and reusable components. AngularJS, on the other hand, is a complete framework that provides a rigid, structured path for building an entire application from the ground up.
So, the real question is whether you need a lightweight, flexible tool for your UI or an all-in-one solution designed for massive projects.
An Introduction to the Frontend Giants
Choosing between React and AngularJS isn't just a technical decision; it's a choice that defines the entire direction of a web development project. Both were born to tackle the complexities of building dynamic, single-page applications, but they come at the problem from completely different philosophical angles. To make the right call, you first have to understand their origins and core principles.
React, which is developed and maintained by Facebook, is often called the "V" (View) in a Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture. It’s not a framework that tells you how to do everything. Instead, it offers a powerful and incredibly efficient way to render UI components and manage their state. This library-first approach gives developers total freedom to pick and choose other tools for things like routing or state management, letting them build a development stack that’s perfectly suited to their needs.
AngularJS (often called Angular 1.x) was Google's opinionated, all-inclusive MVC framework. It was built to be a complete package right out of the box, handing developers a strict structure that covered everything from data binding and dependency injection to directives for extending HTML. While its successor, Angular (2+), is a total rewrite, grasping the original AngularJS philosophy is key to understanding its place among React's early competitors.
This choice has real business implications. The JavaScript framework market is a serious economic engine. In Russia, for example, the market is projected to generate around $76.5 million in 2025, which really shows the commercial weight behind these technologies. Learn more about the JavaScript frameworks market growth.
Before we dive deep, let's start with a quick look at how these two stack up at a high level.
React vs AngularJS High-Level Comparison
This table offers a quick snapshot of the core differences between React and AngularJS, giving you an immediate overview to set the stage for our detailed comparison.
| Attribute | React | AngularJS |
|---|---|---|
| Type | UI Library | Full MVC Framework |
| Maintained By | Google (Legacy) | |
| Core Language | JavaScript (JSX) | JavaScript |
| Data Flow | One-Way Data Binding | Two-Way Data Binding |
| DOM | Virtual DOM | Real DOM |
| Structure | Flexible and Unopinionated | Structured and Opinionated |
This guide will break down these distinctions in much more detail, helping you figure out which tool is the right fit for your specific project.
To get a broader perspective, you can also check out our guide on the best web application frameworks for a look at other popular options.
Comparing Core Architectural Philosophies

To really get to the bottom of the react vs angular js debate, you have to look past the surface-level features and dive into their core philosophies. This is where the two really diverge, and it shapes everything from how a developer works to how the final application performs.
The simplest way to put it is this: React is a library, and AngularJS is a framework. This single distinction is the root of almost every other difference between them.
React has a pretty straightforward, unopinionated philosophy. It gives you an incredibly powerful tool for building user interfaces and then simply gets out of your way. Its architecture is built on a few key pillars that are all about giving developers flexibility and freedom.
AngularJS, on the other hand, is a full-blown, opinionated framework. It hands you a predefined structure for your entire application, telling you how to organise your code, manage your data, and wire everything together. The goal here is to create consistency and standardisation, especially on big projects with large teams.
React: The Unopinionated UI Library
React’s architecture is famously built on components. In a React app, everything is a component—a self-contained, reusable chunk of code that handles its own state and renders a specific piece of the UI. This modular style makes building and maintaining complex interfaces a whole lot easier.
Think of a social media feed. It could be broken down into individual components like <Post>, <CommentList>, and <LikeButton>. Each one manages its own logic, which keeps the overall structure much cleaner and more manageable. To make this work effectively, you really need a solid grasp of writing clean code, as it directly impacts how maintainable a component-based project will be in the long run.
The magic behind React’s performance is the Virtual DOM. Instead of messing directly with the browser’s real DOM—which is notoriously slow—React keeps a lightweight copy of it in memory. When something changes, React updates this Virtual DOM first, figures out the most efficient way to make those changes, and then updates the real DOM in one optimised batch. This process, called reconciliation, cuts down performance overhead dramatically.
Finally, React gave us JSX (JavaScript XML), a syntax extension that lets developers write what looks like HTML right inside their JavaScript files.
const element =
Hello, developer!
;
It might look a bit odd at first, but it keeps a component's markup and logic neatly bundled together. This makes the code more readable and simplifies understanding how the UI relates to the component's state.
Key Takeaway: React’s philosophy is all about being a specialised library for the 'View' layer. It gives you powerful tools for rendering the UI but leaves bigger architectural decisions, like routing or global state management, up to you. The result is maximum flexibility.
AngularJS: The Structured MVC Framework
AngularJS was built around the classic Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern. This design neatly separates an application into three interconnected parts:
- Model: This is where the application's data and business logic live.
- View: The HTML that the user actually sees and interacts with.
- Controller: The bridge between the Model and the View, handling user input and updating the data.
This separation of concerns provides a clear blueprint for building an application, which can be a huge advantage on large, complex projects. You can learn more about how structures like this contribute to a scalable system architecture in our detailed guide.
A defining feature of AngularJS is its two-way data binding. This creates a live, real-time sync between the Model and the View. If a user types something into an input field (the View), the data in the Model updates instantly without you having to write any extra code. And if the Model changes, the View automatically reflects it. It’s powerful, but it can also lead to performance bottlenecks in really complex apps.
AngularJS also leans heavily on directives. These are custom HTML attributes that tell AngularJS to attach specific behaviours to a DOM element. Core directives like ng-model for data binding or ng-repeat for looping over lists essentially extend HTML’s capabilities, letting developers create rich, dynamic templates right in their HTML.
Evaluating Performance and Real-World Speed

Talking about architecture in theory only gets you so far when you’re comparing React vs AngularJS. The real proof is in the performance. How fast does the page load? How slick is the UI when a user starts clicking around? It’s here that the core differences between React’s Virtual DOM and the change detection in AngularJS really come to light.
React’s secret weapon for speed is its Virtual DOM. Instead of messing with the slow and clunky browser DOM every time something changes, React works with a lightweight copy in memory. When a component’s state is updated, React figures out the absolute minimum number of changes needed and then applies them to the real DOM in one smart, optimised batch.
This makes React incredibly quick for applications with a lot of moving parts, like live data dashboards, busy social media feeds, or forms with complex validation. By keeping direct DOM manipulation to a minimum, it delivers a fluid, responsive user experience.
AngularJS and the Digest Cycle Bottleneck
AngularJS, on the other hand, is built on a digest cycle and two-way data binding. To spot changes in your data, it has to periodically run through a whole list of "watchers." When it finds a change, the digest cycle kicks off to update the entire view.
This works just fine for smaller apps, but it can become a serious performance headache as an application gets bigger. If you have thousands of watchers on a single page, the digest cycle can get bogged down and chew through resources. The result? Noticeable UI lag, especially when you’re dealing with large datasets or complex interactions.
In essence, React updates the UI like a surgeon, changing only what's necessary. AngularJS often does a full check-up, which can be massively inefficient when just one small thing has changed. This is a critical distinction for projects where user interaction is constant.
Initial Load Time and Memory Consumption
Initial load time is another performance metric you can't ignore. Because React is a library, its core is naturally smaller than the all-in-one AngularJS framework. This usually means a faster initial page load, since the browser has less JavaScript to download and process before it can show the user anything.
Of course, the final bundle size for a React project really depends on the third-party libraries you pull in. AngularJS comes with a lot of features baked in, which can mean a larger initial bundle but might save you from adding a ton of external dependencies later on.
This performance dynamic is particularly relevant in certain markets. For instance, in Russia, where Google Chrome holds about 47.34% of the browser market, frameworks optimised for modern browsers tend to have an advantage. React’s lightweight core and efficiency fit well with user expectations there. You can explore more about the Russian browser market on gs.statcounter.com.
Real-World Scenarios and Recommendations
So, let's break down which one gets the job done better in specific situations.
- For dynamic, high-interaction SPAs: React is the undisputed winner here. Its Virtual DOM is purpose-built for apps that need constant UI updates without grinding to a halt. Think stock trading platforms or collaborative design tools.
- For large enterprise applications with complex forms: AngularJS can still be a solid choice, but developers have to be careful. You need to actively manage the digest cycle and be stingy with the number of watchers to keep performance in check.
- For mobile applications: On mobile, performance is everything. While this comparison is web-focused, the same principles apply. Rigorous performance testing is a non-negotiable part of the process, as we detail in our comprehensive mobile app testing checklist.
When it comes down to it, React's architecture generally offers a more reliable performance baseline for modern, dynamic web applications. While you can certainly optimise an AngularJS app, it takes a lot more conscious effort from the developer to sidestep the common performance traps tied to its two-way data binding and digest cycle.
Getting to Grips with the Learning Curve and Developer Experience
When you’re weighing up React vs AngularJS, one of the biggest questions for any team is the learning curve. How fast can a developer actually start building features and adding value? The answer really gets to the heart of their completely different philosophies on the developer experience.
For most developers, especially those who already have a solid grasp of JavaScript, React feels like a gentler entry point. Its API is tiny, focused almost entirely on one thing: building UI components. This means developers spend their time writing what feels like standard JavaScript, just sprinkled with JSX, which is a lot more familiar than having to learn a framework-specific templating language from scratch.
AngularJS, on the other hand, demands a much bigger upfront commitment. It’s a complete, all-in-one framework with its own set of rules and concepts. Before you can be productive, you have to get your head around a whole range of topics, including modules, directives, scopes, and dependency injection.
The Initial Onboarding Process
React's learning path feels more gradual for a reason. A developer can become productive after understanding just a handful of core concepts: components, state, and props. The freedom to pick and choose other libraries for things like routing or state management means a team can slot React into their view layer without having to rip out their entire workflow right away.
In contrast, becoming proficient in AngularJS means you have to understand its entire ecosystem. The framework is highly opinionated, which means it has a "correct" way of doing almost everything. While this rigid structure is great for long-term consistency, it creates a much steeper initial hurdle. Developers simply have to learn the "AngularJS way" before they can really be effective.
The real difference in developer experience boils down to this: React asks you to know JavaScript well, while AngularJS asks you to learn AngularJS well. This single distinction massively impacts training time and how quickly a new project can get moving.
Debugging and Tooling Experience
The developer experience doesn't stop after the first few weeks; it bleeds into day-to-day tasks like debugging. Here, React’s one-way data flow is a huge help for troubleshooting. When a bug pops up, you can usually trace the data flowing downwards from parent to child components, making it far simpler to figure out exactly where the state went wrong.
Debugging in AngularJS can be a lot trickier, mostly because of its two-way data binding and the infamous digest cycle. It’s not always clear what triggered a change in the model, since the view can update the model just as easily as the model updates the view. This can lead to some long, frustrating debugging sessions, especially in apps with lots of watchers and complex data interactions.
Documentation and Community Support
Both technologies have massive communities and mountains of documentation, but they feel very different. React's official documentation is lean and focused, which makes sense for a library. The wider community then fills in the gaps with an endless supply of tutorials and third-party tools for everything else you might need.
AngularJS provides incredibly detailed official documentation that covers every single part of the framework. Because it’s a much more structured system, the official guides are usually the first and last place you need to look for answers.
Situational Recommendations:
- For Teams with Strong JavaScript Skills: React is almost always the better fit. Your team can hit the ground running by using what they already know, and they’ll appreciate the flexibility it gives them.
- For Projects Requiring Strict Standardisation: AngularJS offers a rigid structure that can be a real asset for large teams. It forces everyone to build in a consistent, standardised manner, which can make long-term maintenance much simpler—assuming the team is fully trained and on board with its conventions.
A Look at the Tooling and Community Ecosystems

A technology's real power isn't just in its core code; it's in the world that builds up around it. When you compare React vs AngularJS, the differences in their tooling and community support are massive, and they really get to the heart of their opposing philosophies—library versus framework. This isn't just a technical detail; it directly shapes how you'll build, test, and grow your application.
React has always been about freedom and flexibility. It does one thing exceptionally well: managing the view layer. For everything else, from managing your application's state to handling page routing, you're expected to tap into a massive, ever-evolving ecosystem of third-party libraries. This "choose your own adventure" approach lets developers build a completely custom stack that’s a perfect fit for their project.
AngularJS, on the other hand, comes as a more structured, all-in-one package. It arrives with many of the essential tools already built right into the framework, creating a standardised development environment from the start. This opinionated style is designed to enforce consistency, which is a huge plus in big enterprise environments where having everyone on the same page is a top priority.
Building Your Development Stack
With React, the Node Package Manager (npm) is your best friend and the gateway to an almost endless supply of libraries. For state management, Redux was the long-reigning king, though slicker, simpler alternatives like Recoil and Zustand are gaining a lot of ground. Need routing? React Router is the undisputed choice. For server-side rendering to give your SEO and performance a boost, frameworks like Next.js are practically essential.
All this choice allows for incredible innovation, but it also creates a bit of a decision-making headache. Every React team has to carefully research and pick each library, weighing up its maintenance history, documentation quality, and community buzz.
AngularJS makes this whole process much simpler by including most of this functionality right out of the box. It has its own built-in router (ngRoute) and its own way of handling HTTP requests. While you can still use third-party libraries, the core tools are provided and maintained by the Angular team, so there's much less need to go hunting for outside packages.
The core trade-off is crystal clear: React gives you unparalleled choice but adds complexity, while AngularJS offers a stable, unified toolkit but sacrifices flexibility. Your team's preference for customisation versus standardisation is the deciding factor here.
Comparing Tooling for Core Functions
The practical differences really hit home when you look at everyday development tasks. To make this concrete, let’s see how each ecosystem handles key functionalities. It's a great way to see the contrast between React's modularity and AngularJS's integrated approach in action.
Here's a side-by-side look at the common tools and libraries used for key functionalities in both React and AngularJS.
Ecosystem and Tooling Comparison
| Functionality | Popular React Solution(s) | Built-in/Popular AngularJS Solution(s) |
|---|---|---|
| State Management | Redux, Recoil, Zustand, Context API | Built-in $scope and services |
| Routing | React Router | Built-in ngRoute module |
| HTTP Client | Axios, Fetch API | Built-in $http service |
| Testing | Jest, Enzyme, React Testing Library | Karma, Jasmine, Protractor |
| UI Components | Material-UI, Ant Design, Bootstrap | Angular Material, UI Bootstrap |
This table shows how React relies on a constellation of specialised libraries, while AngularJS leans on its own internal, pre-packaged solutions for most core needs.
The Power of Community and Corporate Backing
Both technologies have some serious corporate muscle behind them—Facebook for React and Google for AngularJS. That backing provides a huge amount of long-term stability and guarantees ongoing development.
React’s community, however, is arguably larger and more energetic, with a non-stop flood of new libraries, tutorials, and courses. A 2021 developer survey highlighted this gap, with 40.14% of developers preferring React, while only 22.96% chose Angular, showing just how widespread its adoption has become.
AngularJS might be the older of the two, but it still has a massive and mature community. Its resources tend to be more centralised and focused on the "official" way of doing things within its structured framework. This can actually make it easier for newcomers to find consistent, high-quality answers, as they won't get lost in the sea of options that sometimes overwhelms people in the React world. Ultimately, your project’s success will lean heavily on which of these support styles best clicks with your team’s experience and workflow.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
So, how do you decide between React and AngularJS? It really boils down to your project's specific needs, your team's existing skills, and where you see the project going long-term. There's no single "best" choice, just a better fit for the job at hand. We've already dug into the technical differences, so now let's turn that analysis into a practical decision.
Think of it like this: React gives you a high-performance engine and a box of specialised tools, letting you build whatever you want. AngularJS, on the other hand, gives you a complete, pre-assembled factory line. What you plan to build will dictate which one you need.
When to Choose React
React's flexibility and raw performance make it the clear winner for projects where a dynamic, slick user interface is the main event. Its component-based structure and super-efficient Virtual DOM rendering really come into their own in a few key scenarios.
You should lean towards React if your project involves:
- Dynamic Single-Page Applications (SPAs): If you're building something like a social media feed, an interactive data dashboard, or a real-time collaboration tool, the constant UI updates will benefit hugely from React's speed.
- Strong SEO Requirements: When you pair React with a framework like Next.js for server-side rendering, you get a powerful setup for building fast, indexable websites that play nicely with search engines.
- Mobile App Development: If a mobile app is on your roadmap, starting with React paves a smooth path to building a native application using React Native. This lets you share code and developer talent between web and mobile.
The job market also tells a compelling story. In Russia's frontend landscape in 2024, React is the dominant force, making up around 52% of relevant job postings, while Angular still holds a very respectable 36%. This trend underscores React's strong industry position and the deep pool of available talent.
When to Choose AngularJS
AngularJS is still a powerhouse, especially for large-scale applications where structure, consistency, and a standardised toolkit are non-negotiable. What some see as its rigid, opinionated nature actually becomes a major plus in enterprise settings.
AngularJS is the smarter choice for:
- Large-Scale Enterprise Applications: For complex systems built and maintained by large, often distributed teams, AngularJS's strict MVC architecture enforces a consistent coding style. This makes long-term maintenance much less of a headache.
- Projects Needing a Comprehensive Solution: If your team prefers an all-in-one toolbox with built-in solutions for things like routing, state management, and making HTTP requests, AngularJS provides a stable, unified environment right out of the box.
The core decision in the react vs angular js debate isn’t about which technology is technically superior. It’s about which philosophy better matches your project's scale and your team’s workflow. Go with React's adaptable library for speed and creative freedom, or choose AngularJS's structured framework for enterprise-grade consistency.
As you make these architectural choices, it's vital to think about how your frontend will talk to your backend APIs. For instance, understanding the finer points of HTTP methods like PUT vs PATCH will shape how you design data updates, no matter which framework you end up using. This kind of deep technical thinking is essential for building a truly robust and scalable application. By weighing these use cases against your project's goals, you can make a well-informed choice that sets you up for success from day one.
Frequently Asked Questions About React vs AngularJS
Even after a side-by-side comparison, some practical questions always pop up when you're deciding between React and AngularJS. We'll tackle the most common ones here to help you get over the finish line.
So, is AngularJS completely obsolete now? Let's be direct: for new projects, yes, you should steer clear. While countless large, legacy systems are still chugging along on AngularJS, it is no longer in Long Term Support (LTS). That means no more security patches or new features. Its successor, Angular (version 2 and up), is a ground-up rewrite and the modern standard.
This decision tree infographic breaks down the choice based on your project's most pressing needs.
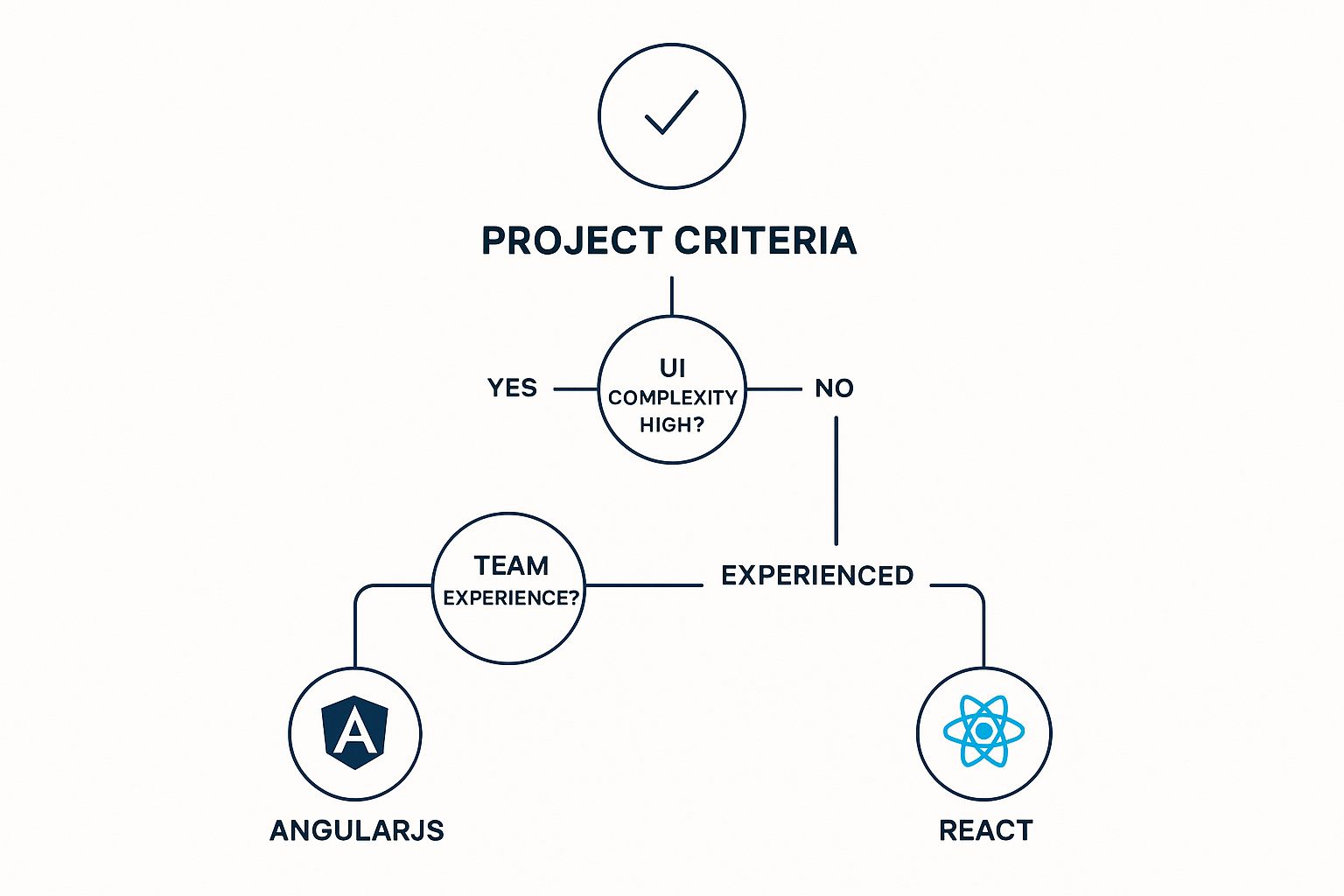
As the graphic illustrates, your final decision often boils down to the complexity of your UI and the experience level of your dev team.
Which Is Better for SEO
Out of the box, neither technology is a silver bullet for Search Engine Optimisation (SEO). Both are client-side, meaning they build the page in the user's browser, which can sometimes make it tricky for search engine crawlers to properly index your content.
However, the React ecosystem has a far more mature and elegant solution to this problem: server-side rendering (SSR). Frameworks like Next.js pre-render pages on the server, sending fully-formed HTML directly to crawlers. While AngularJS has some SSR workarounds, they are clunkier and less common. If organic search traffic is a top priority, React gets the clear edge thanks to its top-tier SSR tooling.
Key Insight: When looking at react vs angular js for SEO, the real question isn't about the library itself, but about the strength of its server-side rendering ecosystem. The React community’s heavy investment in tools like Next.js gives it a massive advantage.
Can You Migrate from AngularJS to React
Yes, it's absolutely possible, but it's important to understand what you're getting into. Migrating from AngularJS to React is not a simple "upgrade"—it's a complete rewrite of your frontend. Their architectures are fundamentally opposed (MVC vs. component-based, two-way vs. one-way data flow), so you can't just translate the code.
Most teams take an incremental approach. They rebuild specific features or components in React and run both frameworks together until the entire application is ported over. This strategy, known as the strangler fig pattern, is the safest way to tackle a migration without disrupting your users.
- Step 1: Set up a new React environment to run alongside the existing AngularJS app.
- Step 2: Pick an isolated feature, like a single page or a settings modal, to rebuild in React.
- Step 3: Use routing to direct users to the new React version of that feature while the rest of the site stays in AngularJS.
- Step 4: Repeat the process, gradually "strangling" the old AngularJS code until nothing is left.
This methodical process makes a massive undertaking manageable, even for large, business-critical applications.
At KP Infotech, we specialise in building high-performance web and mobile solutions with today's leading technologies. Whether you’re starting fresh or migrating a legacy system, our expert team provides the strategic guidance and technical firepower you need. Let's talk about bringing your project to life at https://kpinfo.tech.
